CWDM vs. DWDM
WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexing) is a method of transmitting data from different sources on a single fiber whereby each data channel is carried on its own unique wavelength. A WDM system uses a CWDM or DWDM multiplexer at the transmitter to join various signals together, and a demultiplexer at the receiver to split them apart. Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing (CWDM) and Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) are both mature WDM technologies, using standardized ITU-T wavelengths. This article will make a comparison between them according to their corresponding characteristics and applications.
CWDM is currently well-positioned to help carriers maximize their network capacity in the access, metro and regional network segments. CWDM supports fewer wavelengths than DWDM, but is available at a fraction of the cost of DWDM. This makes CWDM attractive for areas with moderate traffic growth projections. Thus CWDM is the ideal choice for cost efficiently short-haul transmission in telecoms or enterprise networks. While DWDM is designed for long-haul transmission where wavelengths are packed tightly together, providing a high-capacity solution in telecom networks. Generally speaking, DWDM and CWDM are based on the same concept of using multiple wavelengths of light on a single fiber, but differ in the wavelengths spacing, number of channels and the ability to amplify the multiplexed signals in the optical space.
The major difference between them is that DWDM multiplexing systems are made for longer haul transmission, by keeping the wavelengths tightly packed. They can transmit more data over a significantly larger run of cable with less interference than a comparable CWDM system. CWDM cannot travel long distances because the wavelengths are not amplified, and therefore CWDM is limited in its functionality over longer distances. Therefore, DWDM technology is one of the best choices for transporting extremely large amounts of data traffic over long distance in optical networks.
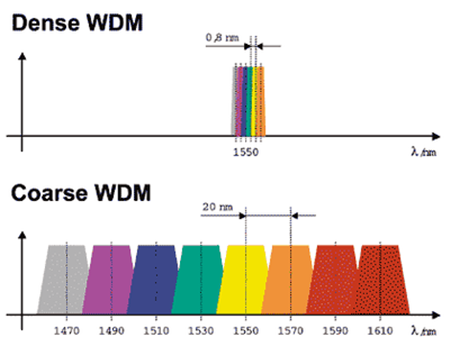
Compared with DWDM which is a more tightly packed WDM system, CWDM has larger wavelengths spacing with fewer wavelengths be transported on the same fiber. For instance, CWDM typically has 20 nm wavelengths spacing while DWDM typically has approximately 0.8 nm, hence can pack 40 plus channels compared to CWDM in the same frequency range. Thus, more channels and higher capacity can be achieved using DWDM.
CWDM systems, on the other hand, use DFB lasers that are not cooled. These systems typically operate from 0 to 70°C with the laser wavelength drifting about 6 nm over this range. This wavelength drift, coupled with the variation in laser wavelength of up to ±3 nm (due to laser die manufacturing processes), yields a total wavelength variation of about ±12 nm. However, DWDM systems require larger cooled DFB lasers for a semiconductor laser wavelength drifts about 0.08 nm/°C with temperature. The use of uncooled lasers causes lower energy consumption, which has positive financial implications for systems operators. For instance, the cost of the battery is minimized with the decreasing of energy consumption, which reduces operating costs. So DWDM systems are more expensive than CWDM systems for the application of cooled lasers.
In conclusion, CWDM and DWDM differ in complexity, offered capacity, cost and the markets they address. Due to its low cost and simple deployment, CWDM is a good fit for access networks and many metro/regional networks. While DWDM increases the distances between network elements, which is a huge benefit for long-haul service providers looking to reduce their initial network investment significantly.